Page 81 - International Perspectives on Effective Teaching and Learning in Digital Education
P. 81
AI in Higher Education: Analysis of Relevant Practices and Their Potential for Green Transition
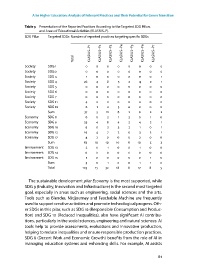
Table 3 Presentation of the Reported Practices According to the Targeted SDG Pillars
and Areas of Educational Activities (KLASIUS–P).
SDG Pillar Targeted SDGs Number of reported practices targeting specific SDGs
KLASIUS–P1 KLASIUS–P KLASIUS–P3 KLASIUS–P4 KLASIUS–P5 KLASIUS–P6 KLASIUS–P7
Total
Society SDG 1
Society SDG
Society SDG 3 1 1
Society SDG 4 6 4 8 5 4 1
Society SDG 5
Society SDG 6
Society SDG 7
Society SDG 11 4
Society SDG 16 6 1 3
Sum 37 5 1 8 6
Economy SDG 8 6 1 1
Economy SDG 9 5 4 8 4 4 1
Economy SDG 1 9 3 1 1
Economy SDG 1 19 4 7 3 1
Economy SDG 17 4
Sum 63 1 19 1 6 1 5 3
Environment SDG 13 1 1
Environment SDG 14
Environment SDG 15 1 1
Sum 3 1 1 1
Total 13 15 3 18 8 17 8 5
The sustainable development pilar Economy is the most supported, while
SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure) is the second most targeted
goal, especially in areas such as engineering, social sciences and the arts.
Tools such as Blender, Midjourney and Teachable Machine are frequently
used to support creative activities and promote technological progress. Oth-
er SDGs in this pilar, such as SDG 1 (Responsible Consumption and Produc-
tion) and SDG 1 (Reduced Inequalities), also have significant AI contribu-
tions, particularly in the social sciences, engineering and natural sciences. AI
tools help to provide assessments, evaluations and innovative production,
helping to reduce inequalities and ensure responsible production practices.
SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) benefits from the role of AI in
managing education systems and enhancing skills. For example, AI assists
81