Page 127 - Glasbenopedagoški zbornik Akademije za glasbo v Ljubljani / The Journal of Music Education of the Academy of Music in Ljubljana: Jakob Jež (1928-) Tokovi sodobne zborovske glasbe, leto 14, zvezek 29 / Year 14, Issue 29, 2018
P. 127
Helmut Schaumberger, HOW TO SING PROFESSIONALLY WITH CHILDREN ...
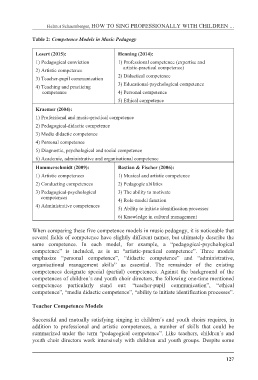
Table 2: Competence Models in Music Pedagogy
Losert (2015): Henning (2014):
1) Pedagogical conviction 1) Professional competence (expertise and
artistic-practical competence)
2) Artistic competence
2) Didactical competence
3) Teacher-pupil communication
3) Educational-psychological competence
4) Teaching and practicing
competence 4) Personal competence
5) Ethical competence
Kraemer (2004):
1) Professional and music-practical competence
2) Pedagogical-didactic competence
3) Media didactic competence
4) Personal competence
5) Diagnostic, psychological and social competence
6) Academic, administrative and organisational competence
Hammerschmidt (2009): Bastian & Fischer (2006):
1) Artistic competences 1) Musical and artistic competence
2) Conducting competences 2) Pedagogic abilities
3) Pedagogical-psychological 3) The ability to motivate
competences 4) Role-model function
5) Ability to initiate identification processes
4) Administrative competences
6) Knowledge in cultural management
When comparing these five competence models in music pedagogy, it is noticeable that
several fields of competence have slightly different names, but ultimately describe the
same competence. In each model, for example, a “pedagogical-psychological
competence” is included, as is an “artistic-practical competence”. Three models
emphasize “personal competence”, “didactic competence” and “administrative,
organisational management skills” as essential. The remainder of the existing
competences designate special (partial) competences. Against the background of the
competences of children´s and youth choir directors, the following one-time mentioned
competences particularly stand out: “teacher-pupil communication”, “ethical
competence”, “media didactic competence”, “ability to initiate identification processes”.
Teacher Competence Models
Successful and mutually satisfying singing in children´s and youth choirs requires, in
addition to professional and artistic competences, a number of skills that could be
summarized under the term “pedagogical competence”. Like teachers, children´s and
youth choir directors work intensively with children and youth groups. Despite some
127
Table 2: Competence Models in Music Pedagogy
Losert (2015): Henning (2014):
1) Pedagogical conviction 1) Professional competence (expertise and
artistic-practical competence)
2) Artistic competence
2) Didactical competence
3) Teacher-pupil communication
3) Educational-psychological competence
4) Teaching and practicing
competence 4) Personal competence
5) Ethical competence
Kraemer (2004):
1) Professional and music-practical competence
2) Pedagogical-didactic competence
3) Media didactic competence
4) Personal competence
5) Diagnostic, psychological and social competence
6) Academic, administrative and organisational competence
Hammerschmidt (2009): Bastian & Fischer (2006):
1) Artistic competences 1) Musical and artistic competence
2) Conducting competences 2) Pedagogic abilities
3) Pedagogical-psychological 3) The ability to motivate
competences 4) Role-model function
5) Ability to initiate identification processes
4) Administrative competences
6) Knowledge in cultural management
When comparing these five competence models in music pedagogy, it is noticeable that
several fields of competence have slightly different names, but ultimately describe the
same competence. In each model, for example, a “pedagogical-psychological
competence” is included, as is an “artistic-practical competence”. Three models
emphasize “personal competence”, “didactic competence” and “administrative,
organisational management skills” as essential. The remainder of the existing
competences designate special (partial) competences. Against the background of the
competences of children´s and youth choir directors, the following one-time mentioned
competences particularly stand out: “teacher-pupil communication”, “ethical
competence”, “media didactic competence”, “ability to initiate identification processes”.
Teacher Competence Models
Successful and mutually satisfying singing in children´s and youth choirs requires, in
addition to professional and artistic competences, a number of skills that could be
summarized under the term “pedagogical competence”. Like teachers, children´s and
youth choir directors work intensively with children and youth groups. Despite some
127