Page 176 - International Perspectives on Effective Teaching and Learning in Digital Education
P. 176
Mojca Žefran and Silva Bratož
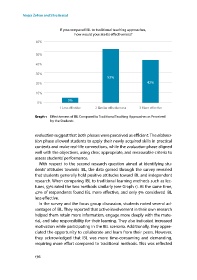
If you compared IBL to traditional teaching approaches,
how would you rate its e ectiveness?
60%
50%
40%
30%
53%
20% 42%
10%
5%
0%
1 Less e ective 2 Similar e ectiveness 3 More e ective
Graph 1 Effectiveness of IBL Compared to Traditional Teaching Approaches as Perceived
by the Students
evaluation suggest that both phases were perceived as efficient. The elabora-
tion phase allowed students to apply their newly acquired skills in practical
contexts and make real-life connections, while the evaluation phase aligned
well with the objectives, using clear, appropriate, and measurable criteria to
assess students’ performance.
With respect to the second research question aimed at identifying stu-
dents’ attitudes towards IBL, the data gained through the survey revealed
that students generally hold positive attitudes toward IBL and independent
research. When comparing IBL to traditional learning methods such as lec-
tures, 53% rated the two methods similarly (see Graph 1). At the same time,
4% of respondents found IBL more effective, and only 5% considered IBL
less effective.
In the survey and the focus group discussion, students noted several ad-
vantages of IBL. They reported that active involvement in their own research
helped them retain more information, engage more deeply with the mate-
rial, and take responsibility for their learning. They also indicated increased
motivation while participating in the IBL scenario. Additionally, they appre-
ciated the opportunity to collaborate and learn from their peers. However,
they acknowledged that IBL was more time-consuming and demanding,
requiring more effort compared to traditional methods. This was reflected
176