Page 109 - World Heritage and Tourism Innovation
P. 109
Anton Gosar Layers of Tourism in Protected Ecosystems of Slovenia
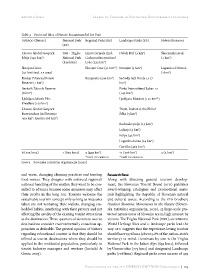
Table 3 Protected Sites of Nature Recommended for Visit
UNESCO (Nature) National Park Regional Parks (RP) Landscape Parks (KP) Natural Reserves
(NP)
Unesco Global Geopark TNP - Triglav Inner Carniola (incl. Debeli Rtič (3 km ) Škocjanski zatok
2
2
Idrija (294 km ) National Park Cerknica Intermittend (1 km )
2
(839 km2) Lake (222 km )
2
2
Škocjan Caves Škocjan Cave (31 km *) Strunjan (4 km ) Lagunes of Ormož
2
(31 km ; incl. RP area) (1km )
2
2
2
Krokar Primeval Forest Kozjansko (206 km ) Sečovlje Salt Ponds LP (7
Reserve (1 km ) km )
2
2
Snežnik Ždrocle Reserve Pivka Intermittend Lakes-17
(8 km ) (140 km )
2
2
Ljubljana Marsh Pile- Ljubljana Marshes (150 km *)
2
Dwellers (150 km )
2
Unesco Global Geopark Tivoli, Rožnik & the Hill of
Karawanken (in Slovenija Šiška (5 km )
2
2
2
409 km ; Austria 568 km )
Radensko polje (15 km )
2
Lahinja (3 km )
2
Kolpa (43 km )
2
Logarska dolina (24 km )
2
Goričko (462 km )
2
6 (773 km2) 1 (839 km2) 3 (429 km ) 11 (706 km ) 2 (2 km )
2
2
2
* incl. in UNESCO * incl. in UNESCO
Source Sovenska turistična organizacija (2020)
and water, changing cleaning practices and treating Research Base
food-wastes. They disagree with enforced regional/ Along with directing general tourism develop-
national handling of the matter; they want to be con- ment, the Slovenian Tourist Board (STO) publishes
sulted in advance because some measures may affect award-winning catalogues and promotional mate-
their profits in the long run. Tourists welcome the rials highlighting the Republic of Slovenia’s natural
sustainable tourism concept only as long as measures and cultural assets. According to the STO brochure
taken are not venturing their wallets, changing em- Outdoor Slovenia: Movements in the Nature (Sloven-
bedded habits, interfering with their privacy and not ska turistična organizacija, 2020), 23 large-scale pro-
affecting the quality of the existing tourist attractions tected nature areas of Slovenia are in high interest by
at the destination. Three-quarters of visitors to tourist visitors. The Triglav National Park (TNP), six UNESCO
destinations consider environmentally conscious ap- World Heritage Sites and 11 landscape parks lead the
proaches as desirable. The general opinion of visitors way. STO suggests that the experience-loving tourists
regarding educational content is that they should be should have 1976 km2 (about 9.8% of the nation-state’s
offered at tourist destinations where they should be territory) in mind. Dominant by size is the Triglav
applied to the residential population, particularly to National Park in the Julian Alps (839 km2), followed
tourist industry managers and workers (Jurinčič & by Unesco sites (773 km2) and designated Landscape
Gosar, 2003). parks (706 km2). Regional parks cover an area of 429
Proceedings of the 7th UNESCO UNITWIN Conference | 105